Insulation
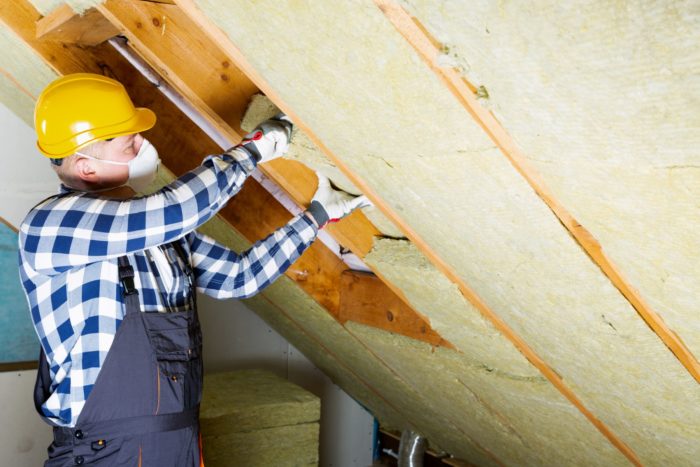
Insulation Installation
Whether you’re building or buying a home, it is important to understand the value of a quality insulation system. Insulation is vital to your home’s value and can greatly impact your comfort as well as utility costs over time. Nine out of ten U.S. homes are under-insulated, and many homeowners are turning to experts to properly seal their home against thermal and air loss. Many homeowners who upgrade their home insulation report saving an average of $200 a year on their home energy costs, which can add up quickly.
By evaluating the types of insulation available, you can make an informed decision about insulation installation based on your specific needs and budget. After insulation installation, your energy bills may decrease and your home’s value may increase. Insulation reduces the costs of heating and cooling by over 40%, which means installing additional insulation in your home can pay for itself within five or six years.
Different Rooms, Different Insulation
There are five main locations in which you can install insulation in your home: the attic, walls, floors, crawl space, and basement. Sealing air leaks in floors, attics, and crawl spaces cuts household air leakage by 45% according to DOE Building America. Air leakage accounts for 25% to 40% of your home’s heating and cooling capacity, which means your HVAC costs may be higher than necessary.
Attic
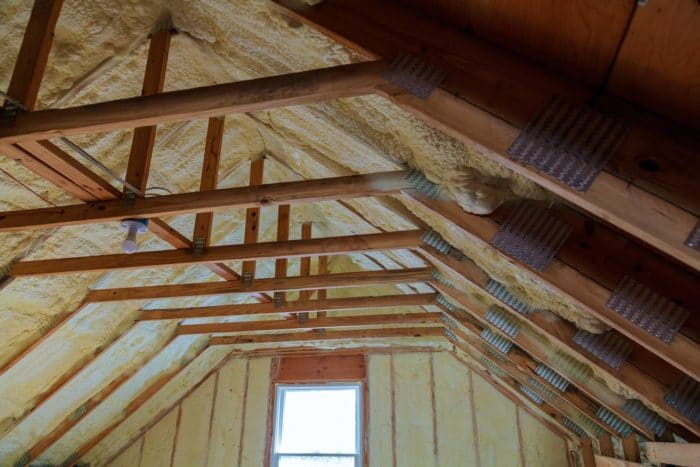
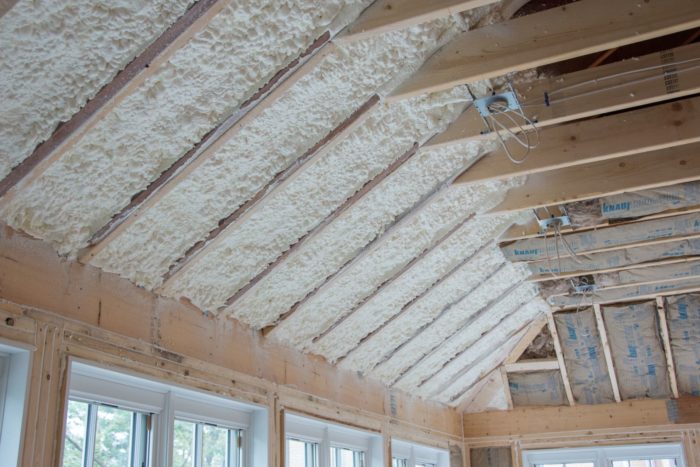
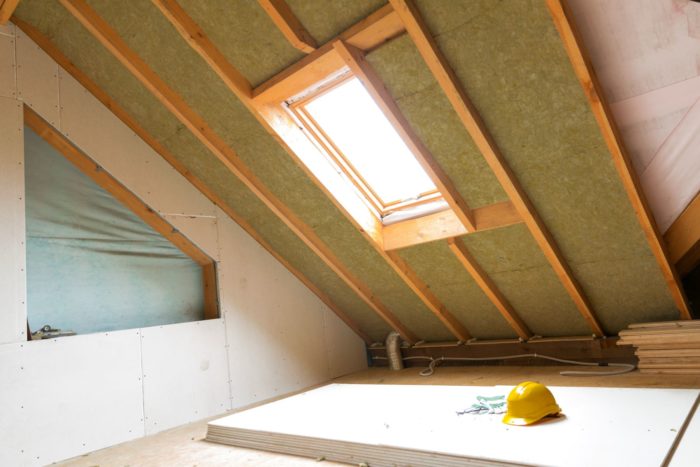
Whether you live in a warm or cold climate, the attic is the most important place to insulate in a home. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, attic insulation is particularly important in older homes (built before 1980) where existing levels of insulation may require reinforcement. Nearly 85% of a home’s heat loss occurs in the attic. Batt, blown-in, and spray foam insulation are commonly installed in attics.
A reflective radiant barrier can be added to your attic insulation system to increase its energy efficiency. As much as 20% of your home’s energy bill can be reduced with quality roof insulation. Reflective barrier roof insulation reduces attic temperatures in the summer. In warmer climates, it reflects and reduces the radiant energy of the sun.
Basement
A properly insulated basement can save you time and money, as well as provide you with a comfortable living space. If you have an unfinished basement, you add insulation to the home’s foundation. Proper basement insulation provides crucial protection against moisture, helping prevent harmful mold and mildew problems. Batt and spray foam insulation are commonly installed in basements.
Crawl Space
Proper crawl space insulation keeps living spaces comfortable. A crawl space is also the most commonly overlooked weak point in a home that can let in unwanted air and heat. You can install batt, blown-in, and spray foam insulation in a crawl space. Blown-in and spray foam insulation are a good choice for smaller, hard-to-reach places in a crawl space.
Floors
As much as 10% of the heat in a room can be lost through uninsulated ground floors. Any floor over an unheated or unconditioned space needs to have adequate thermal insulation. Many homeowners overlook this key component to a good home insulation system, particularly when it comes to floors over basements, porches, storage spaces, and garages. Batt, blown-in, and spray foam insulation types can all be installed in floors to help reduce thermal loss.
Walls
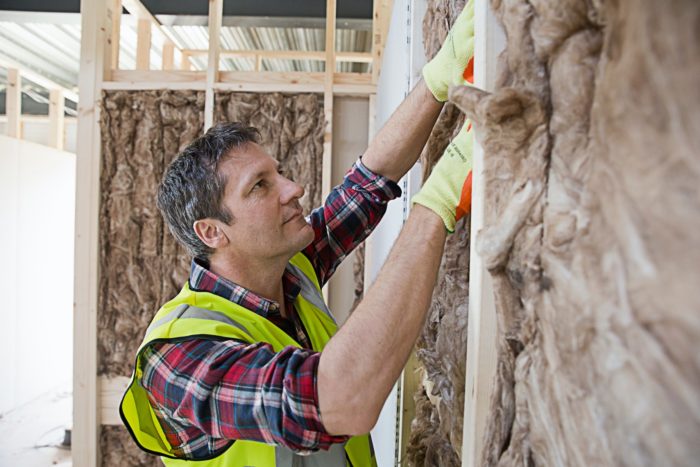
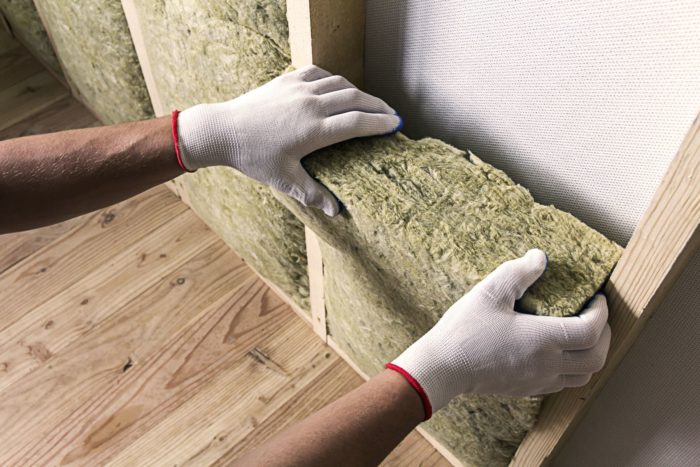
Insulating your walls is one of the least expensive ways to improve your home’s energy efficiency. Proper wall insulation can reduce your home’s energy loss by two-thirds. Wall insulation also prevents noise from carrying throughout your house. Batt, blown-in, and spray foam insulation are good choices for wall insulation. Rigid board insulation may also be installed around the outside of a home’s frame during construction to prevent heat loss caused by thermal bridging.
Air Ducts
External air vents and internal ductwork can be another weak point in your home’s insulation system. Air loss through ducts can account for nearly 30% of your home’s energy consumption. Reduce thermal loss by properly insulating your air ducts and sealing the edges of external connection points with spray foam insulation. Seal and insulate internal ductwork that travels through unconditioned spaces.
Types of Insulation
Homeowners can control utility bills by learning about energy efficient home insulation design. Understanding the types of insulation available to you will help guide your insulation decisions, especially if you’re designing a net-zero energy system or high-efficiency home. Compare important features, materials, and installation processes to help meet the needs of your insulation project while sticking to your budget.
Batts & Rolls
Blankets and rolled insulation are easy for contractors to install and can be used in the same spaces as blown-in and sprayed insulation. Fiberglass batts are among the most commonly used forms of insulation as they are a cost-effective way to protect your home against thermal loss, especially when paired with sealing tape. Batts and rolls can also be made with wool or plastic fibers.
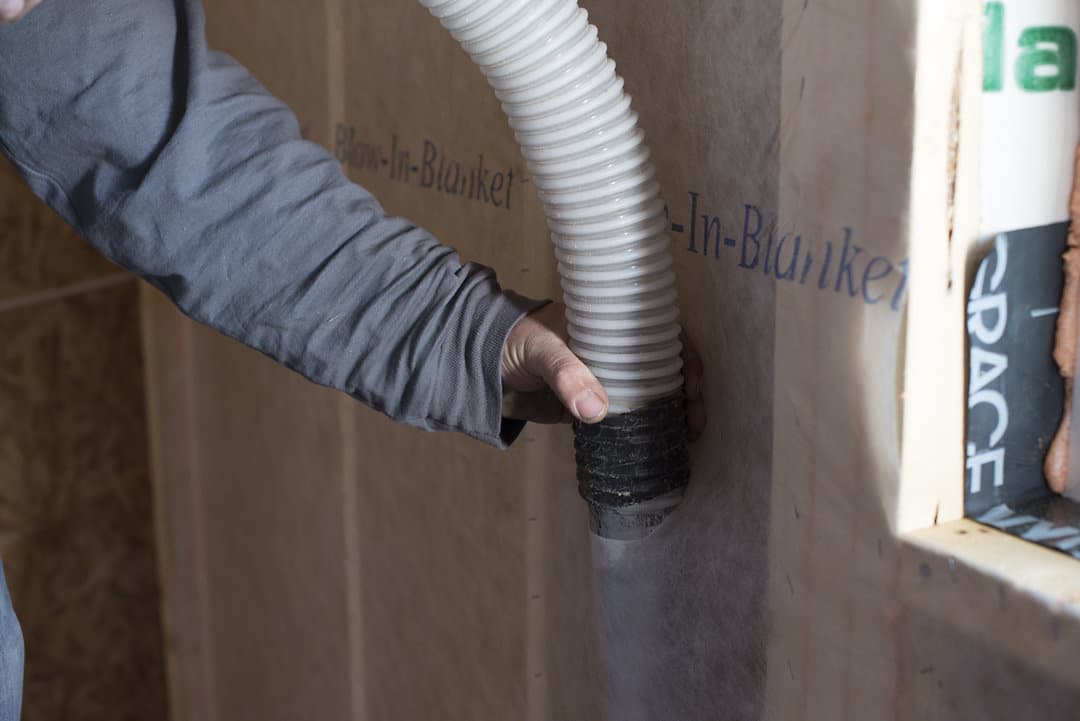
BIBS Insulation & Spray Application
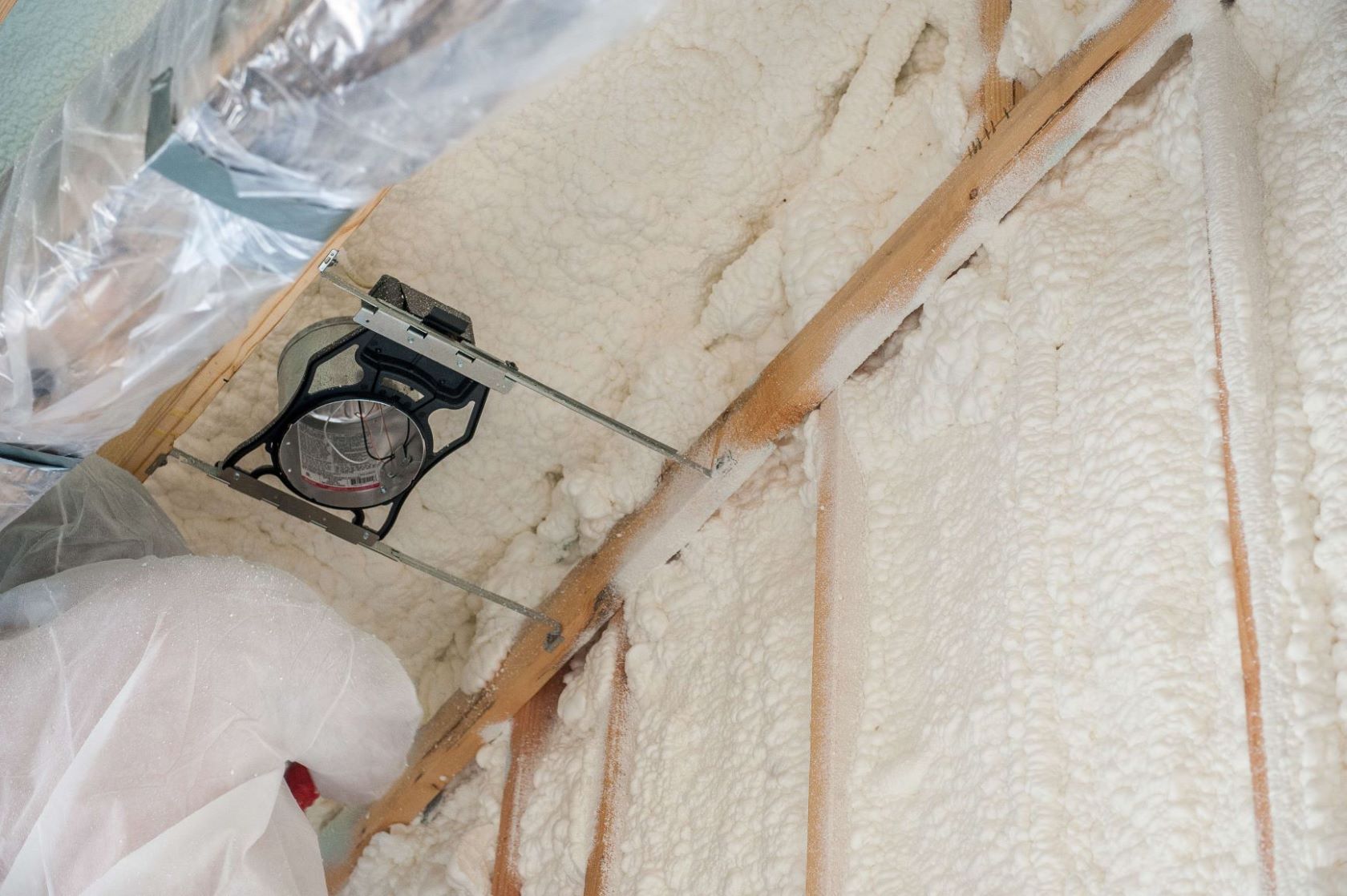
BIBS systems work by blowing loose-fill insulation into a netted wall space. Blown-in (“loose fill”) and sprayed insulation types are both ideal for post construction in crawl spaces, attics, basements, and other areas. Blown-in and sprayed insulation are often used when there are hard-to-move obstructions. Blown-in blanket systems (BIBS) are typically made of fiberglass wool or plant-based cellulose fibers and offer high-density thermal protection.
Rigid Board Insulation
Rigid board insulation takes the form of structural sheets and is often used around the outside of a home’s frame during construction to create a thermal seal. Rigid board insulation has excellent fire resistance and is typically made from a variety of materials including polyisocyanurate (polyiso) and polystyrene. Rigid board insulation also comes in mineral and fiber board varieties.
Reflective Barrier Systems
Reflective barrier systems work by keeping heat away from your home. Reflective barriers are ideal for framing windows and other areas that experience heat retention and loss. Radiant barriers are also often used beneath roof lines and in attics to protect homes from hot rooftop sun. Reflective barriers are a complement to structural insulation systems, adding a layer of protection to other forms of insulation.
Important Properties of Insulation
R-value is a measure of insulation’s ability to resist heat traveling through it. The higher the R-value, the better the thermal performance of the insulation. However, R-value is not the only determination of insulation’s quality. Four factors determine the quality and overall effectiveness of insulation:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Air filtration
- Radiation
Spray foam, for example, may have a low R-value and yet it is still one of the best insulation types in the industry due to its sealing properties. Your regional climate, including seasonal temperature ranges, humidity, and air quality, will help you determine which insulation works best for your needs.
What Your Region Means for Insulation Installation
Different regions require different levels of insulation. Becoming familiar with the R-value of various insulation options will help you choose the insulation that best fits your needs. Warmer climates will not require insulation with higher R-values, which can save you from spending unnecessarily. Conversely, opting for higher R-values in colder climates will help you stay comfortable during long winters.
The map below shows the most cost-effective levels of insulation for the different climate zones in the U.S. Based on your zone, use the table to find out how much insulation you need.
The higher the R-value of insulation, the more thermal insulating capacity it has. Zones 1, 2, and 3 make up the southern portions of the U.S. and have an average suggested minimum insulation rating of R-30 in attics and R-13 along floors. Zones 4 to 7, which cover the northern half of the country, suggest that attic insulation have a minimum R-38 rating and floor insulation have a minimum R-25 rating.
| Climate | R-Value |
| Warm Climates | R-30 to R-49 |
| Moderate Climates | R-38 to R-60 |
| Cold Climates | R-49 to R-60 |
What To Expect
Insulation contractors will walk you through the process of estimating, scheduling and performing inspections for your insulation project. Expect the installation team to keep you informed during all stages of your project and to explain what may be needed from you. In some cases, you may need to be out of your home to follow safety protocol.
When looking for insulation contractors, be prepared with a list of the areas of your home and, if possible, their dimensions. Insulation installation is not a one-size-fits-all project. Each area of the home requires unique materials, depth, and technical considerations. Be sure to include attics, crawlspaces, and basements, which can often be weak points in a home’s insulation system. Let the insulation installers know of any specific gaps or cracks you’re aware of so that they can be sure to address these areas.
If you are not sure where to get started, TruTeam can help! Our insulation contractors are familiar with which types of insulation work in each space of a home. For example, basement insulation should have moisture and mold-resistant properties, while attics and roof spaces may need a reflective radiant barrier layer to protect against rooftop heat.
Insulation Installation: How Long Does It Take?
For an insulation job to be done well, it should not be rushed. However, it is understandable to want the job done as quickly as is reasonably possible. Luckily, 95% of insulation materials are manufactured in the U.S. with American-made materials, so your insulation is unlikely to be delayed by shipping or low stock.
A contractor’s estimate should fall within the following time frames. These timelines can be impacted if the contractor needs to perform additional services like removal of old insulation.
| Typical Installation Job | Typical Timeframe |
| Attic Insulation | 1-2 days |
| Crawl Space | 2-3 hours |
| Wall Spray Foam Injection | 2-5 hours |
| Cavity Wall Blown-In | 1 day max |
Insulation Installers Near You
As a leading installer of insulation in the United States, TruTeam’s local installers are ready to help with any insulation projects. Our experienced insulation professionals bring their local expertise to your doorstep. TruTeam’s building science experts are trained to know which insulation materials will get you the results that you want. If you’re ready to start your insulation project, contact TruTeam today to get a free quote from a local insulation professional.
Ready to get started? Get a contractor you can trust. Contact your local TruTeam branch today for all your installation needs.
The Team You Can Trust
Get Your Quote


Installers
Insulation Materials
Understanding the relative benefits of the many insulation materials available can help guide your project choices.
Spray Foam Insulation
Celebrated for its easy application and premium air sealing abilities, polyurethane spray foam insulation offers a number of advantages. It can be applied to hard-to-reach spaces and is used to seal smaller features like outlets, pipes, and gaps. Spray foam insulation expands after application, creating a highly efficient seal around your home’s thermal weak points.
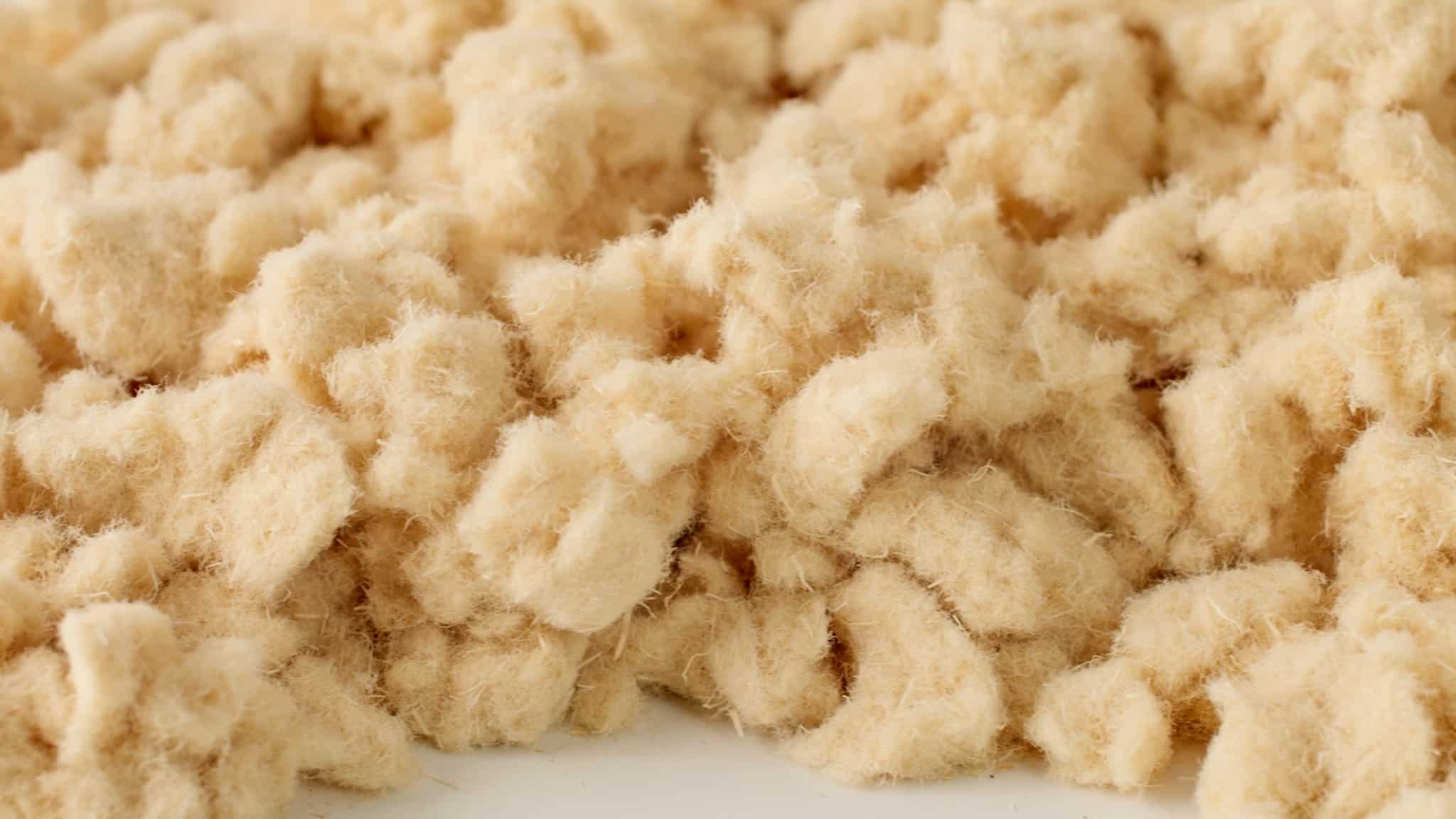
Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass offers a high R-value, long-term durability, and relatively low upfront costs. As the most commonly used insulation type, fiberglass insulation comes in rolled batts or blown-in (BIBS) wool fiber, and rigid board forms. It is a highly versatile choice for your insulation system.
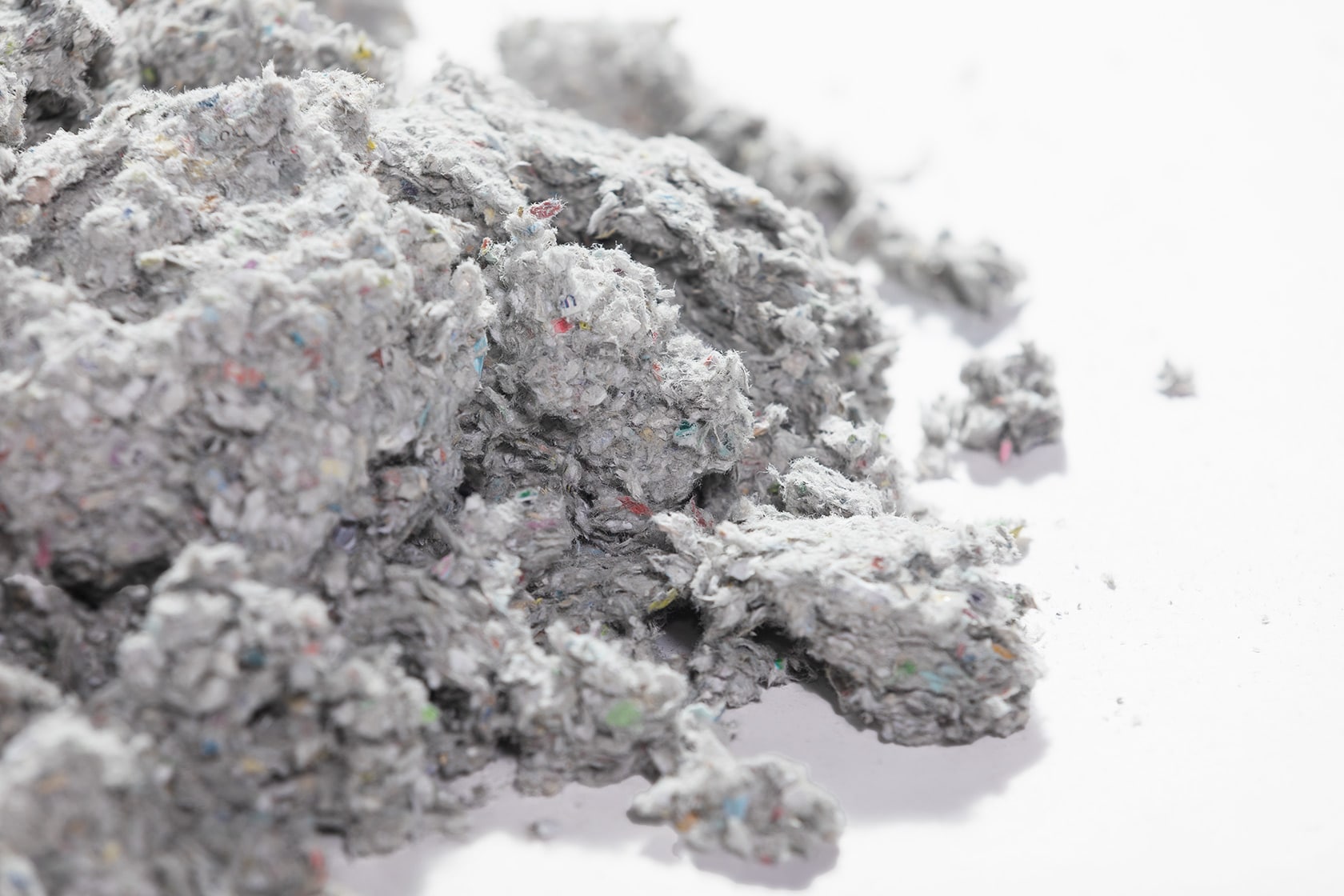
Cellulose Insulation
Celebrated for its sustainability, cellulose insulation is made entirely of plant-based material, most commonly recycled newspaper that is treated for fire-resistance. Cellulose insulation is an eco-friendly choice for residential insulation. It can be applied in a wet or dry application using blown-in system techniques or dry rolled batts.
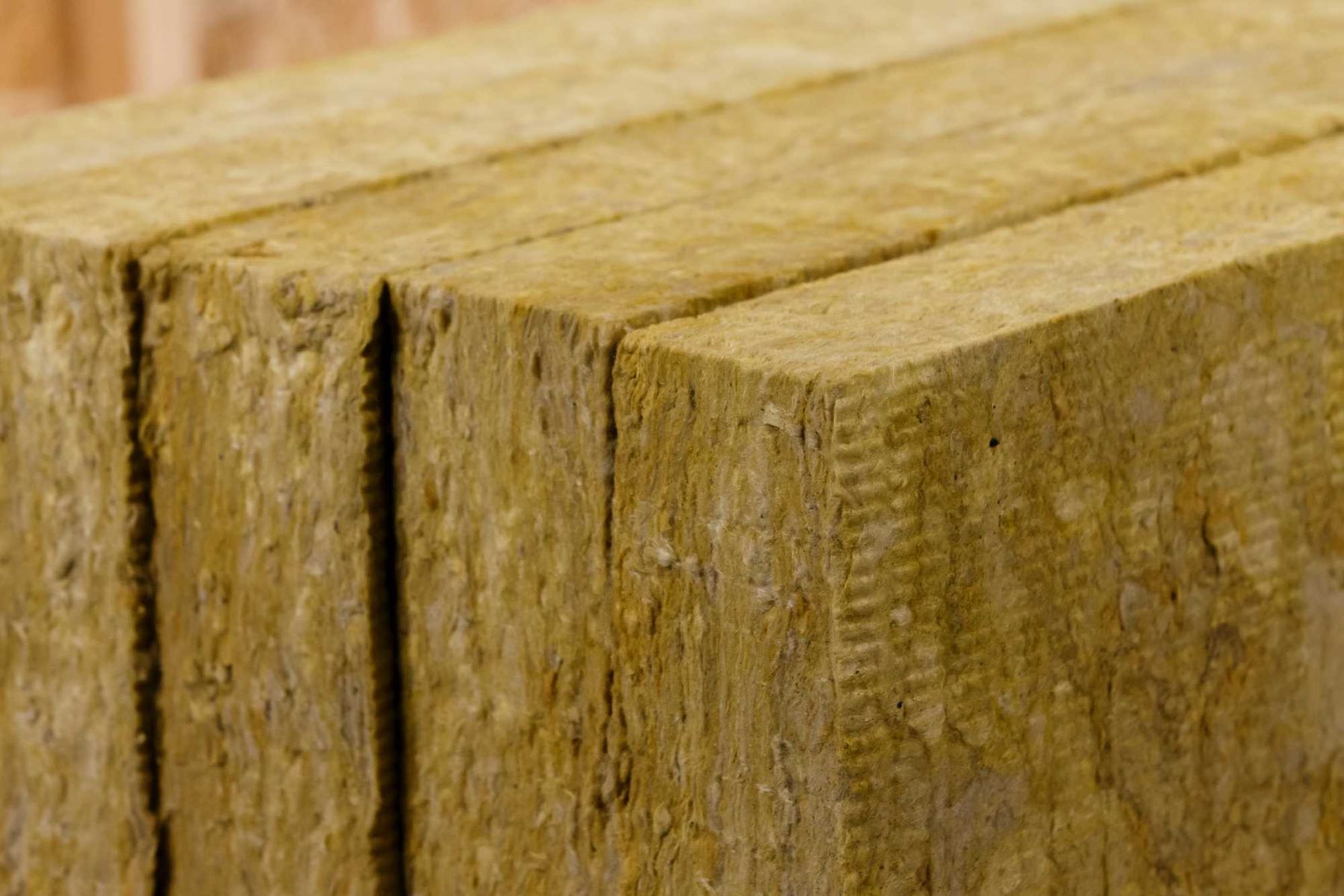
Mineral Wool Insulation
Mineral wool, also called “rock wool,” is primarily made of volcanic rock such as basalt or recycled slag from steel mills. Like fiberglass, mineral wool comes in fibrous, easy-to-install batts or rigid boards. However, it contains far more recycled materials (up to 70%) and offers better sound-dampening, waterproofing, and fireproofing properties. Mineral wool insulation is installed via friction fitting, which means it doesn’t require stapling to hold it in place.
















